Log in to a Linux server with an SSH private key on a Windows client
You should now have a idrsa.pub file which contains your new public SSH key. Add SSH key to your VM. In the previous step, you generated an SSH key pair. Select Use existing public key in the dropdown for SSH public key source so that you can use the public key you just generated. Take the public key and paste it into your VM setup, by copying. These cannot be brute-forced – they are simply too complex. If you can, disable password logins in your “sshdconfig” file (on the server) and use keys instead. In case you travel and can’t carry your laptop with you, just keep your private key on a USB stick and attach it to your physical keychain. Overview Public key authentication is a way of logging into an SSH/SFTP account using a cryptographic key rather than a password.
Authored by: Brint Ohearn
Ssh Use Private Key File Download
This article demonstrates how to load an SSH private key into PuTTY in orderto connect to a Linux® server. You need the followingsoftware to complete this task:
- PuTTY: A client for managing SSH sessions
- PuTTYgen: A tool for managing and creating SSH key pairs
To download both tools, see Download PuTTY: latestrelease.
Note: These instructions apply to using PuTTY on the Windows® operating system.For information about using SSH private keys on Linux and OS X®operating systems, see Log in with an SSH Private Key on Linux andMac.
Save your private SSH key to a text file
As a part of your deployment, Rackspace might have provided you with an SSHprivate key for you to use to authenticate against your newly deployedLinux servers. You must save this private key to a text file. This typeof file is called a key file.
Open a text editor, paste your SSH private key, and save the file.
Your SSH private key should look similar to the key in the following image:
You need to include all of the text that appears in the image in your key file.Load your SSH private key in PuTTY Key Generator
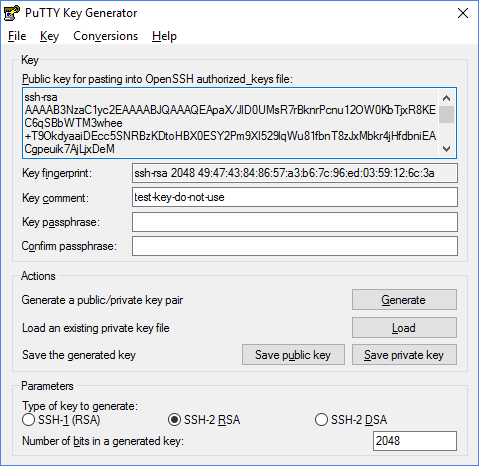
Use the following steps to load your SSH private key in PuTTY Key Generator:
Launch PuTTY Key Generator.
In the Actions section, click Load to load an existing private keyfile. Change the file type to search for to All Files.
Select the key that you saved to a text file earlier and click Open.
A confirmation displays after PuTTYgen successfully imports the privatekey. Click OK to dismiss the message.
Enter a unique key passphrase in the Key passphrase field, then enterthe same passphrase again in the Confirm passphrase field. You areprompted for this passphrase whenever you log in to a server by using yourSSH private key.
Click Save private key, then enter a file name in the Saveprivate key as dialog box to save it for use with PuTTY.
Note: We strongly recommend that you keep the default settings.
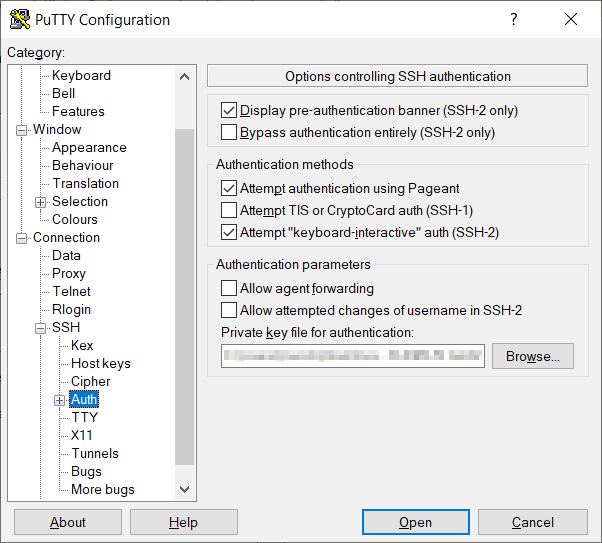
Log in to PuTTY by using your SSH private key
Use the following steps to log in to PuTTY by using your SSH private key:
Enter a name for the session and click Save.
Note: You can use any name that you want. This example names thesession based on the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the server to whichthe user is connecting.
Click Connection > Data in the left navigation pane and set theAuto-login username to root.
Click Connection > SSH > Auth in the left navigation pane andconfigure the SSH private key to use by clicking Browse under Privatekey file for authentication.
Navigate to the location where you saved your SSH private key file, selectthe file, and click Open.
The file path for the SSH private key file now displays in the Privatekey file for authentication field.
Click Session in the left navigation pane, then click Save in theLoad, save or delete a stored session section.
Click Open to begin your session with the server.
If you saved your SSH private key with a passphrase, you’re prompted toenter that passphrase. An alert displays indicating that the server’s hostis not cached. Click Yes to continue the connection.
©2020 Rackspace US, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License
This tutorial explains the Passwordless SSH using Public Key and Private Key in Linux.
SSH stands for Secure SHELL, is a protocol used to connect remote hosts to login or performing some tasks using scripts.
When we want to automate some tasks on remote hosts using scripts from a centralized server like Jenkins/Ansible or any Linux Server, we may require a password less connection between the remote hosts and the centralized Server.
In this tutorial, we will learn to create Passwordless SSH login using public key and private key. Follow the step by step guide to make your ssh connection passwordless.
This tutorial will work for Linux Destro such as Centos, Ubuntu, Redhat, Amazon Linux(AWS EC2) and Other as well.
Recommended Read:How to Install Jenkins on Ubuntu
Also Read : Git Tutorial for beginners (Part I)
Scenario
We have one Local Machine and one Remote Server.We will setup a passwordless connection to login Remote Server from the local Machine.
Ssh Use Private Key File Opener
Perform following steps on the remote Server
Step 1– Create an User and login or login as an existing user.
$ useradd devops
$ su – devops
Step 2 – Generate a key pair ( Public key and Private Key) using ssh-keygen command.
Before running this command make sure you are on home directory of the user.If not you can go to the home directory by cd ~ command.
$ cd ~
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
It will ask for some details. Do not put anything here and press ENTER only.
By ls -al command you can see a hidden directory .ssh and two files namely id_rsa and id_rsa.pub inside .ssh directory are created.Here id_rsa is the Private key and id_rsa.pub is the Public Key.
Private key(id_rsa) is kept at source computer(local machine) from where you have to ssh. Public Key(id_rsa) is kept at Destination Server(Remote Server) , the Server you want to access.
Step 3- Create a file name authorized_keys in side .ssh directory and copy the content of id_rsa.pub file to authorized_keys file.
Go to .ssh directory
$ cd ~/.ssh/
Create an empty file name authorized_keys
$ touch authorized_keys
Copy the content of id_rsa.pub to authorized_keys
$ cat id_rsa.pub > authorized_keys
Check the authorized_keys file if contents are copied.
$cat authorized_keys
Step 4 – Change the permission of authorized_keys
$ chmod 600 authorized_keys
Step 5– Copy the content of id_rsa file
Use cat command to display the content of id_rsa and copy its content.
$ cat id_rsa
On the local Machine
Step 1– Create a file and paste the content of id_rsa copied from remote server inside this file. You can use nano command to perform this action.
Create a file name devops.key using nano command , paste the content and pres Ctrl+X to save and close the file.
$ nano devopys.key
Step 2 – SSH remote Server from local machine without using password.
$ sudo ssh -i path-to-private-key [email protected]
$ sudo ssh -i devops.key [email protected]
I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and learned Passwordless SSH login using public key and private key. If you think this is really helpful, please do share this to other as well. Please also share your valuable feedback, comment or any query in the comment box.I will really happy to resolve your all queries.
Thank You
If you think we helped you or just want to support us, please consider these:-
Connect to us: Facebook | Twitter
